by:Takuma Yoshioka、Saiful Aziz、Poom Kerdsang
This article is the fourth in a series of articles from GVA LPC providing basic legal information to foreign companies and individuals planning to do business in Japan. This series of articles will highlight Japanese laws and regulations, which are central to their need to smoothen their business venture into the Japanese market.
For foreign companies that intend to do business in Japan that involves the importation of food products into Japan, it should be noted that in Japan, there is no requirement to obtain a specific or special ‘license’ to be able to have the right to import most food products into Japan, except for the importation products classified as alcoholic beverages, which a license is required. However, depending on the type of the food products, an ‘import approval’ may also be required. The Foreign Exchange and Foreign Trade Act (“FEFTA”) prescribed that a cabinet order may be issued to control the importation of a certain type as to achieve the sound development of foreign trade and the national economy or to fulfill obligations under the treaties and other international agreements the Japan government has entered.
Generally, all importation of food products into Japan requires the importer to provide an ‘import notification’ as prescribed under the Food Sanitation Act (“FSA”). The FSA requires an import notification for the importation of food products that are to be served for the purpose of marketing or to be used in business. This requirement extends to the importation of food products that are to be used as a marketing strategy and will be given for free to unspecified individuals.
The importation process of food products into Japan can be divided into three stages, starting with the first stage, the submission of the import notification by the importer. The submission must be made to the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare’s (“MHLW”) quarantine station that is holding the food product in question, and all submissions should be made before the process of customs clearance. In the second stage, upon receiving the import notification, the inspection authority will decide if an inspection should be conducted on the food product. If an inspection is needed, the inspection authority will issue the respective order to confirm compliance with the FSA. At this stage, the inspection authority will, among others, (i) validate all facts that were detailed in the import notification, (ii) ensure there is no breach of relevant laws (see chart below), and (iii) ensure that the food products meet Japanese manufacturing standards. Finally, in the third stage, if the inspection authority determines that the food products comply with all necessary laws, the MHLW quarantine station, where the notification was initially submitted, will issue a “notification certificate” to the importer and the importation of the food product will follow its course.
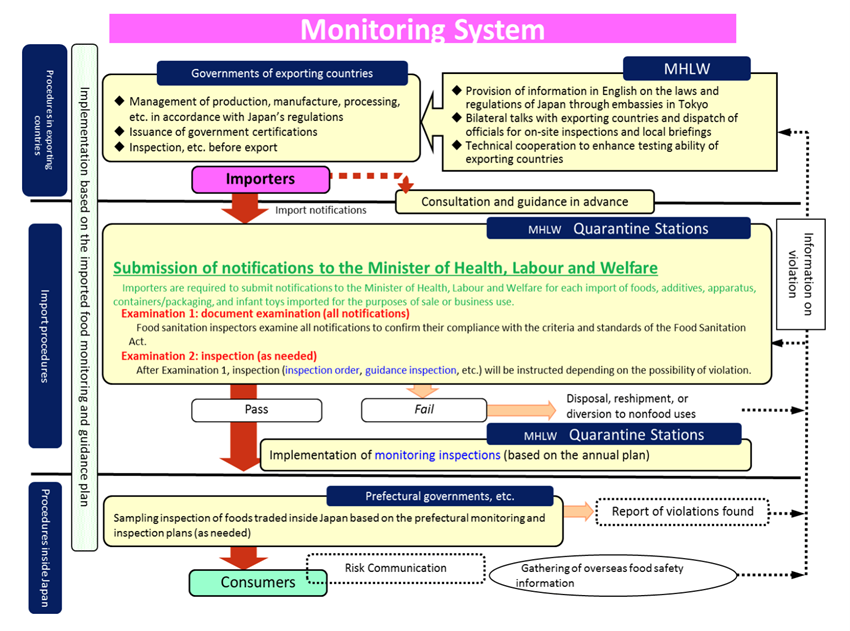
(Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare/Import Procedure under Food Sanitation Act)
In addition to the FSA and FEFTA, different food products will be subjected to various laws and regulations. These laws and regulations will be considered during the inspection stage of the importation process; therefore, companies must confirm in advance what laws or regulations will be imposed on their food products. For reference, below is the list of laws that are applicable based on the type of food product.
Types of Food Products | Laws | |
|---|---|---|
Vegetables, fruits, grain, beans, teas, coffee beans (raw), herbs, spices, etc. | Plant Protection Act 1950 | |
Meat and processed meat products | Act on Domestic Animal Infectious Diseases Control 1951 | |
Liquor | Liquor Tax Act 1953 | |
Rice, wheat, etc. | Plant Protection Act 1950 | Act on Stabilization of Supply, Demand and Price of Staples Food 1994 |
Salt | Salt Industry Act 1996 | |
Sugar and Starch | Act on Price Adjustment of Sugar and Starch 1965 | |
Butter, skim milk, etc. | Act on Temporary Measures Concerning Price for Producers of Milk for Manufacturing Use 1965 | |
Processed Food Products | Food Labeling Act 2013 | |
The information provided in this article is made for reference purposes only. It is advisable to consult a legal professional to understand in detail the implications of the laws and regulations regarding the importation of food products in Japan.
-end










